December 8, 2025
What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and How Does It Impact Your Costs?
10 min read

Ever wondered why some websites load instantly while others leave you staring at a spinning wheel? The secret often lies in a Content Delivery Network (CDN), a system of distributed servers strategically positioned across the globe to deliver web content to users with lightning speed.
Think of a CDN network as a chain of digital warehouses. Instead of forcing every visitor to fetch data from a single, distant location, a CDN stores copies of your website's content on multiple servers worldwide. When someone accesses your site, the content is delivered from the server closest to them, dramatically cutting down loading times.
CDNs, today, have become essential infrastructure rather than a luxury. Users expect websites to load in under three seconds. If it’s any slower, you risk losing potential customers. Search engines like Google also factor page speed into their rankings, making CDNs crucial for visibility and competitiveness.
This blog explores what a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is and how it affects cost & performance for businesses of all sizes. We'll break down how CDNs work, examine their impact on your bottom line, and help you understand whether implementing a CDN makes financial and operational sense for your specific needs. From bandwidth savings to enhanced security, you'll discover why CDNs have become indispensable in modern web infrastructure.
Understanding CDNs
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a system of servers located in various parts of the world. These servers, called edge servers or Points of Presence (PoPs), work together to deliver web content to users from the nearest location. When someone visits your website and requests content, the CDN automatically directs that request to the closest edge server. This server then either serves cached content directly or fetches it from your main server if necessary.
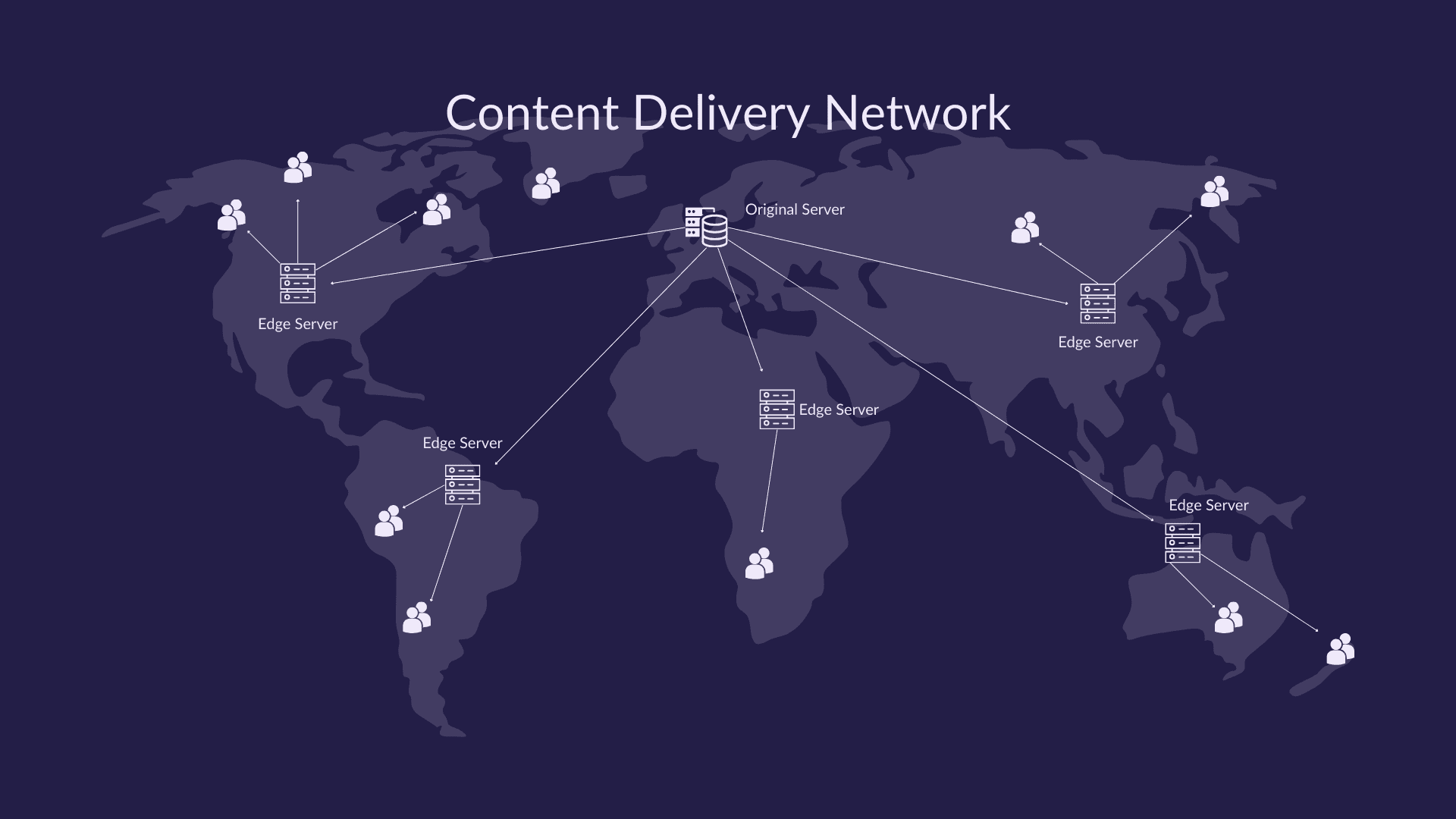
How CDNs Work
User Request: When a user wants to access content from your website, they send a request.
CDN Routing: The CDN identifies the closest edge server to the user and routes the request to that server.
Content Delivery: The edge server either has a cached copy of the requested content and serves it directly or retrieves it from your origin server if it's not cached.
This architecture fundamentally changes how content reaches end users. Instead of every visitor connecting to a single origin server, potentially located thousands of miles away, they connect to a nearby edge server that holds a copy of your content. This distributed approach makes the delivery process more efficient and resilient.
Also read: What Is Cloudfront and How Does It Work?
Benefits of Using a CDN for Website Performance
1. Slashing latency through geographic distribution
Distance matters in digital communication. Every mile between a user and your server adds milliseconds to the loading time. A visitor in Tokyo accessing a server in New York experiences significantly longer load times than someone in Boston making the same request. CDNs eliminate this geographic penalty by positioning content closer to users.
Consider a global e-commerce site: without a CDN, a customer in Sydney might wait 2-3 seconds for product images to load from a US-based server. With a CDN, those same images load from a Sydney edge server in under 500 milliseconds. This reduction in latency directly translates to faster page load times, with studies showing that even a 100-millisecond improvement can increase conversion rates by up to 7%.
2. Transforming user experience and retention
Speed shapes perception. Users form opinions about your website within the first few seconds of interaction, and slow loading times create immediate frustration. The benefits of CDN for website performance extend far beyond technical metrics, they directly influence how visitors perceive your brand and whether they return.
Research consistently demonstrates the connection between speed and engagement:
53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load
A 1-second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions
Pages that load in 2 seconds have an average bounce rate of 9%, while pages taking 5 seconds see bounce rates jump to 38%
CDNs help businesses stay within these critical performance windows. When users experience consistently fast load times, they browse more pages, spend more time on site, and complete more transactions. This improved experience builds trust and encourages repeat visits, creating a positive cycle that benefits both user satisfaction and business metrics.
3. Managing traffic surges without breaking a sweat
Traffic spikes can cripple unprepared infrastructure. A viral social media post, a successful marketing campaign, or seasonal shopping event can send visitor numbers soaring from hundreds to hundreds of thousands in minutes. Without proper distribution, this sudden influx overwhelms origin servers, causing slowdowns or complete outages.
CDNs excel at handling these scenarios through load distribution. When traffic surges occur, the CDN spreads requests across multiple edge servers rather than funneling everything to a single origin point. Each edge server handles a portion of the load, preventing any single point of failure.
During a product launch, for instance, a CDN might serve cached product pages, images, and videos from dozens of edge locations simultaneously. This distribution means your origin server only handles dynamic requests, like checkout processes or account updates, while the CDN manages the bulk of static content delivery. The result? Your site remains responsive even when traffic multiplies tenfold.
The benefits of CDN for website performance become especially apparent during unexpected traffic events.
Cost Advantages with CDN Implementation
The financial benefits of implementing a CDN content delivery network extend far beyond the performance gains. When CDN providers distribute your content across their geographically distributed network of servers, they fundamentally transform your cost structure in ways that directly impact your bottom line.
Reducing bandwidth costs
Bandwidth costs represent one of the largest expenses for websites serving global audiences. Every time a user requests content from your origin server, you're paying for that bandwidth. CDNs dramatically reduce these costs by serving cached content from edge servers, the delivery nodes closest to your users. Instead of repeatedly transmitting the same images, videos, and web pages from your origin server across continents, the CDN's storage nodes maintain copies at strategic locations worldwide. This architecture means you're only paying for bandwidth once to populate the CDN, rather than for every individual user request.
Lowering origin server infrastructure expenses
The cost advantages of using CDN become even more apparent when examining origin server infrastructure expenses. Traditional hosting setups require substantial investment in server capacity to handle peak traffic loads. With a CDN handling the majority of requests through its network of delivery nodes and control nodes, your origin servers experience significantly reduced load. This translates to:
Lower hardware requirements and reduced need for expensive server upgrades
Decreased energy consumption and cooling costs for your data centers
Reduced need for additional server instances during traffic spikes
Less frequent scaling of infrastructure resources
Creating operational efficiency
The benefits of CDN for website performance create a ripple effect on operational costs. When CDNs efficiently handle both static content (through caching at edge locations) and dynamic content (through optimized routing and real-time processing), your infrastructure operates more efficiently. This efficiency means you can maintain smaller, more cost-effective server configurations while still delivering exceptional user experiences across global markets.
Security Enhancements Provided by CDNs
In addition to improving performance and reducing costs, CDNs offer important security benefits that many businesses overlook when considering their infrastructure needs. The same distributed design that makes CDNs effective for delivering content also serves as a strong defense against various online threats.
1. DDoS attack mitigation through distributed infrastructure
CDN providers build their networks specifically to absorb and deflect Distributed Denial of Service attacks before they reach your origin servers. When malicious traffic floods your website, the geographically distributed network of servers acts as a buffer, spreading the attack across multiple delivery nodes and storage nodes rather than overwhelming a single point of failure. This distributed approach means that even during a significant attack, legitimate users can still access cached content from edge locations nearest to them.
The control nodes within CDN architecture continuously monitor traffic patterns, identifying suspicious activity in real-time. When an attack is detected, the network can automatically route malicious requests away from your origin nodes while maintaining service availability for genuine visitors. This capability proves particularly valuable for businesses that can't afford downtime, as the CDN essentially becomes your first line of defense.
2. Encrypted data transmission across the network
Modern CDN content delivery networks implement SSL/TLS encryption by default, securing data as it travels between users and edge servers. This encryption layer protects sensitive information from interception, especially important when handling user login credentials, payment information, or personal data. The encryption happens at the network edge, meaning users benefit from secure connections without the performance penalty typically associated with encryption processing on origin servers.
Many CDN providers also offer Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities integrated directly into their delivery nodes. These firewalls filter malicious requests, block SQL injection attempts, and prevent cross-site scripting attacks before they reach your infrastructure. The combination of encryption, traffic filtering, and distributed architecture creates multiple security layers that would be expensive and complex to implement independently.
Modern Trends in CDN Technology Evolution
The CDN landscape has transformed dramatically as cloud CDN solutions reshape how content reaches end users. Traditional CDNs relied on fixed infrastructure, but today's cloud-integrated systems offer unprecedented flexibility. Organizations can now scale their content delivery capacity up or down based on real-time demand, paying only for resources they actually use. This shift eliminates the need for costly upfront investments in hardware and allows businesses to expand globally without establishing physical data centers in every region.
Edge computing represents another significant leap in modern trends in CDN technology evolution. Rather than simply caching static content, edge servers now process data and execute code closer to users. This distributed computing model enables:
Real-time data processing with minimal latency
Personalized content delivery based on user location and device type
Advanced security filtering before requests reach origin servers
IoT device support with reduced bandwidth consumption
The convergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning at the edge adds another dimension to CDN capabilities. Smart caching algorithms predict which content users will request next, pre-loading resources before they're needed. These systems analyze traffic patterns to optimize routing decisions dynamically, ensuring each request takes the fastest possible path through the network. The result is a more responsive, intelligent infrastructure that adapts to changing conditions without manual intervention.
Choosing the Right CDN Provider for Your Business Needs
Selecting a CDN provider requires careful evaluation of multiple factors that directly impact both performance and your bottom line. The decision extends beyond simple price comparisons, it demands a thorough assessment of technical capabilities that match your specific requirements.
Key evaluation criteria include:
Geographic coverage: Ensure the provider maintains points of presence (PoPs) in regions where your audience concentrates. A CDN with limited coverage in your target markets defeats the purpose of faster content delivery.
Pricing models: Different providers structure costs around bandwidth consumption, request volume, or hybrid approaches. Understanding these models helps predict expenses as traffic scales.
Performance metrics: Look for providers offering real-time analytics, cache hit ratios, and latency measurements. These insights prove essential for optimization decisions.
API and integration capabilities: Your CDN should seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure, content management systems, and development workflows.
Support and SLA guarantees: Response times during outages and guaranteed uptime percentages protect your business continuity.
Final Thoughts
Content Delivery Networks have transformed how businesses deliver digital content, creating a win-win scenario for both performance and budget management. By distributing content across strategically positioned edge servers, CDNs dramatically reduce latency while simultaneously cutting bandwidth costs at the origin server level. The numbers speak for themselves: faster page loads translate to better user engagement, higher conversion rates, and improved search engine rankings.
The strategic value of implementing a CDN extends beyond immediate technical benefits. Organizations gain:
Cost predictability through reduced infrastructure demands and bandwidth optimization
Scalability to handle traffic surges without expensive emergency upgrades
Enhanced security protecting against costly DDoS attacks and data breaches
Global reach enabling expansion into new markets without physical infrastructure investments
[Request a demo and speak to our team]
[Sign up for a no-cost 30-day trial]
[Check out our free resources on FinOps]
[Try Amnic AI Agents today]
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and how does it work?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system of geographically distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their location. When a user requests content, the CDN routes the request to the nearest server, reducing latency and speeding up content delivery.
How does using a CDN improve website performance?
Using a CDN improves website performance by slashing latency through geographic distribution, enhancing user experience and retention by delivering content faster, and managing traffic surges efficiently without overwhelming your origin server.
What are the cost benefits of implementing a CDN for my website?
Implementing a CDN can reduce bandwidth costs by caching content closer to users, lower origin server infrastructure expenses by offloading traffic, and create operational efficiencies that collectively decrease overall website maintenance costs.
How do CDNs enhance website security?
CDNs enhance security by mitigating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks through their distributed infrastructure and ensuring encrypted data transmission across the network using SSL/TLS protocols, protecting data integrity and user privacy.
What are the latest trends in CDN technology?
Modern CDN technology has evolved with cloud-based solutions offering greater scalability, improved performance optimizations, enhanced security features, and integration capabilities with emerging technologies to meet dynamic business needs.
How do I choose the right CDN provider for my business?
Choosing the right CDN provider involves evaluating factors such as geographic coverage, performance reliability, security features, cost-effectiveness, support services, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure to ensure optimal delivery aligned with your business goals.








